How To Exploit PHP Remotely To Bypass Filters & WAF Rules
Learn about the possibilities that PHP gives us to exploit and execute code remotely in order to bypass filters, input sanitization, and WAF rules.

In the last three articles, I’ve been focused on how to bypass WAF rule set in order to exploit a remote command execution. In this article, I’ll show you how many possibilities PHP gives us in order to exploit a remote code execution bypassing filters, input sanitization, and WAF rules. Usually when I write articles like this one people always ask “really people write code like this?” and typically they’re not pentesters. Let me answer before you ask me again : YES and YES.
This is the first of two vulnerable PHP scripts that I’m going to use for all tests. This script is definitely too easy and dumb but it’s just to reproducing a remote code execution vulnerability scenario (probably in a real scenario, you’ll do a little bit more work to reach this situation):

Obviously, the sixth line is pure evil. The third line tries to intercept functions like system, exec or passthru (there’re many other functions in PHP that can execute system commands but let’s focus on these three). This script is running in a web server behind the CloudFlare WAF (as always, I’m using CloudFlare because it’s easy and widely known by the people, this doesn’t mean that CloudFlare WAF is not secure. All other WAF have the same issues, more or less…). The second script will be behind ModSecurity + OWASP CRS3.
Trying to read /etc/passwd
For the first test, I try to read /etc/passwd using system() function by the request /cfwaf.php?code=system(“cat /etc/passwd”);

As you can see, CloudFlare blocks my request (maybe because the “/etc/passwd”) but, if you have read my last article about uninitialized variable, I can easily bypass with something like cat /etc$u/passwd

CloudFlare WAF has been bypassed but the check on the user’s input blocked my request because I’m trying to use the “system” function. Is there a syntax that let me use the system function without using the “system” string? Let’s take a look at the PHP documentation about strings!
PHP String escape sequences
\[0–7]{1,3} sequence of characters in octal notation, which silently overflows to fit in a byte (e.g. “\400” === “\000”)
\x[0–9A-Fa-f]{1,2} sequence of characters in hexadecimal notation (e.g. “\x41")
\u{[0–9A-Fa-f]+} sequence of Unicode codepoint, which will be output to the string as that codepoint’s UTF-8 representation (added in PHP 7.0.0)
Not everyone knows that PHP has a lot of syntaxes for representing a string, and with the “PHP Variable functions” it becomes our Swiss Army knife for bypassing filters and rules.
PHP Variable functions
PHP supports the concept of variable functions. This means that if a variable name has parentheses appended to it, PHP will look for a function with the same name as whatever the variable evaluates to, and will attempt to execute it. Among other things, this can be used to implement callbacks, function tables, and so forth.
this means that syntaxes like $var(args); and “string”(args); are equal to function(args);. If I can call a function by using a variable or a string, it means that I can use an escape sequence instead of the name of a function. Here an example:

the third syntax is an escape sequence of characters in a hexadecimal notation that PHP converts to the string “system” and then it converts to the function system with the argument “ls”. Let’s try with our vulnerable script:

This technique doesn’t work for all PHP functions, variable functions won’t work with language constructs such as echo, print, unset(), isset(), empty(), include, require and the like. Utilize wrapper functions to make use of any of these constructs as variable functions.
Improve the user input sanitization
What happens if I exclude characters like double and single quotes from the user input on the vulnerable script? Is it possible to bypass it even without using double quotes? Let’s try:

as you can see on the third line, now the script prevents the use of “ and ‘ inside the $_GET[code] querystring parameter. My previous payload should be blocked now:

Luckily, in PHP, we don’t always need quotes to represent a string. PHP makes you able to declare the type of an element, something like $a = (string)foo; in this case, $a contains the string “foo”. Moreover, whatever inside round brackets without a specific type declaration, is treated as a string:

In this case, we’ve two ways to bypass the new filter: the first one is to use something like (system)(ls); but we can’t use “system” inside the code parameter, so we can concatenate strings like (sy.(st).em)(ls);. The second one is to use the $_GET variable. If I send a request like ?a=system&b=ls&code=$_GET[a]($_GET[b]); the result is: $_GET[a] will be replaced with the string “system” and $_GET[b] will be replaced with the string “ls” and I’ll able to bypass all filters!

Let’s try with the first payload (sy.(st).em)(whoami);

and the second payload ?a=system&b=cat+/etc&c=/passwd&code=$_GET[a]($_GET[b].$_GET[c]);

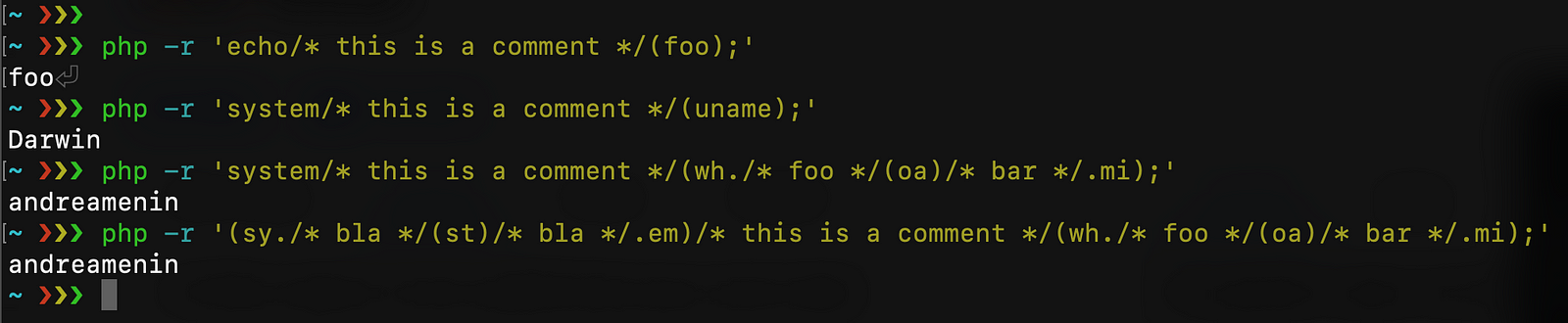
In this case is not useful, but you can even insert comments inside the function name and inside the arguments (this could be useful in order to bypass WAF Rule Set that blocks specific PHP function names). All following syntaxes are valid:
get_defined_functions
This PHP function returns a multidimensional array containing a list of all defined functions, both built-in (internal) and user-defined. The internal functions will be accessible via $arr[“internal”], and the user-defined ones using $arr[“user”]. For example:

This could be another way to reach the system function without using its name. If I grep for “system” I can discover its index number and use it as a string for my code execution:

obviously, this should work against our CloudFlare WAF and script filters:

Array of characters
Each string in PHP can be used as an array of characters (almost like Python does) and you can refer to a single string character with the syntax $string[2] or $string[-3]. This could be another way to elude rules that block PHP functions names. For example, with this string $a=”elmsty/ “; I can compose the syntax system(“ls /tmp”);

If you’re lucky you can find all the characters you need inside the script filename. With the same technique, you can pick all chars you need with something like (__FILE__)[2]:


OWASP CRS3
Let me say that with the OWASP CRS3 all becomes harder. First, with the techniques seen before I can bypass only the first paranoia level, and this is amazing! Because the Paranoia Level 1 is just a little subset of rules of what we can find in the CRS3, and this level is designed for preventing any kind of false positive. With a Paranoia Level 2 all things becomes hard because of the rule 942430 “Restricted SQL Character Anomaly Detection (args): # of special characters exceeded”. What I can do is just execute a single command without arguments like “ls”, “whoami”, etc.. but I can’t execute something like system(“cat /etc/passwd”) as done with CloudFlare WAF:


Previous Episodes
Web Application Firewall Evasion Techniques #1
https://medium.com/secjuice/waf-evasion-techniques-718026d693d8
Web Application Firewall Evasion Techniques #2
https://medium.com/secjuice/web-application-firewall-waf-evasion-techniques-2-125995f3e7b0
Web Application Firewall Evasion Techniques #3
https://www.secjuice.com/web-application-firewall-waf-evasion/
If you liked this post, please share and follow:
Twitter: @AndreaTheMiddle
GitHub: theMiddleBlue
LinkedIn: Andrea Menin


